Introduction to Ethical Hacking
Ethical hacking is an increasingly vital field in the realm of cybersecurity, essential for safeguarding both individuals and organizations from digital threats. Often referred to as “white hat hacking,” ethical hacking involves identifying and addressing security vulnerabilities in computer systems, all while adhering to legal standards and obtaining necessary permissions. This practice is crucial for protecting sensitive data against malicious attacks.
As cybercrime continues to rise, ethical hackers play a pivotal role in fortifying defenses. By employing techniques similar to those of malicious hackers, they aim to preemptively identify and mitigate potential threats. Whether you are a beginner looking to grasp the fundamentals or a professional seeking to enhance your expertise, this article will provide a comprehensive overview of key concepts, types of hackers, and essential steps to embark on a career in ethical hacking.
By examining the distinctions between ethical and malicious hackers, as well as the methodologies and tools employed in this domain, you will be better equipped to navigate the complex landscape of cybersecurity. Join us in this exploration and discover how you can contribute to creating a safer digital environment.
What is an Ethical Hacker?
An ethical hacker is a trained professional hired to deliver top-tier cybersecurity to individuals, businesses, and governments by legally infiltrating their systems and identifying vulnerabilities. Enrolling in an ethical hacking course can help you build a career in this field. Obtain details about cybersecurity courses and pursue training to grasp the fundamentals.
What Are the Fundamental Concepts of Ethical Hacking?
The fundamental concepts of ethical hacking not only differentiate it from other hacking practices but also establish a framework for understanding its principles and methodologies. Before exploring the various “types of hackers” and the processes they employ, it is crucial to first develop a comprehensive overview of these key concepts, as they underpin the ethical standards and practices that guide this important field.
- Legality – Before beginning the process of ethical hacking, hackers should get due permission and legal approval (a MUST do).
- Scope – Ethical hacking can be extensive or shallow depending upon the client’s requirement. Understanding this scope is important before starting the task.
- Report – Once the process of hacking is complete, all the vulnerabilities or security issues should be duly reported to the concerned teams.
- Data Privacy – Ethical hackers often come across data and sensitive information and, therefore, may require signing a contract before they begin working.
Types of Hackers
What are The Three Main Types of Hackers?

White Hat Hackers
White hat hackers are the one who is authorized or certified hackers who work for the government and organizations by performing penetration testing and identifying loopholes in their cybersecurity. They also ensure the protection from the malicious cyber crimes. They work under the rules and regulations provided by the government, that’s why they are called Ethical hackers or Cybersecurity experts.
Black Hat Hackers
lack Hat Hackers – As the name suggests, these types of hackers try to gain unauthorized access to security systems and data systems with the intent to cause harm. Their objective can be stealing sensitive information (which they can sell illegally), halt the operations process of a firm, damage the system permanently, etc. All of this is an illegal and punishable offense
Grey Hat Hackers
They sometimes access to the data and violates the law. But never have the same intention as Black hat hackers, they often operate for the common good. The main difference is that they exploit vulnerability publicly whereas white hat hackers do it privately for the company.One criticism of Grey Hat hackers is that their actions can still cause harm. Even if they do not steal or damage data, their unauthorized access to computer systems can still disrupt operations and cause financial losses for companies. Additionally, there is always the risk that a Grey Hat hacker will accidentally cause damage while attempting to identify vulnerabilities.
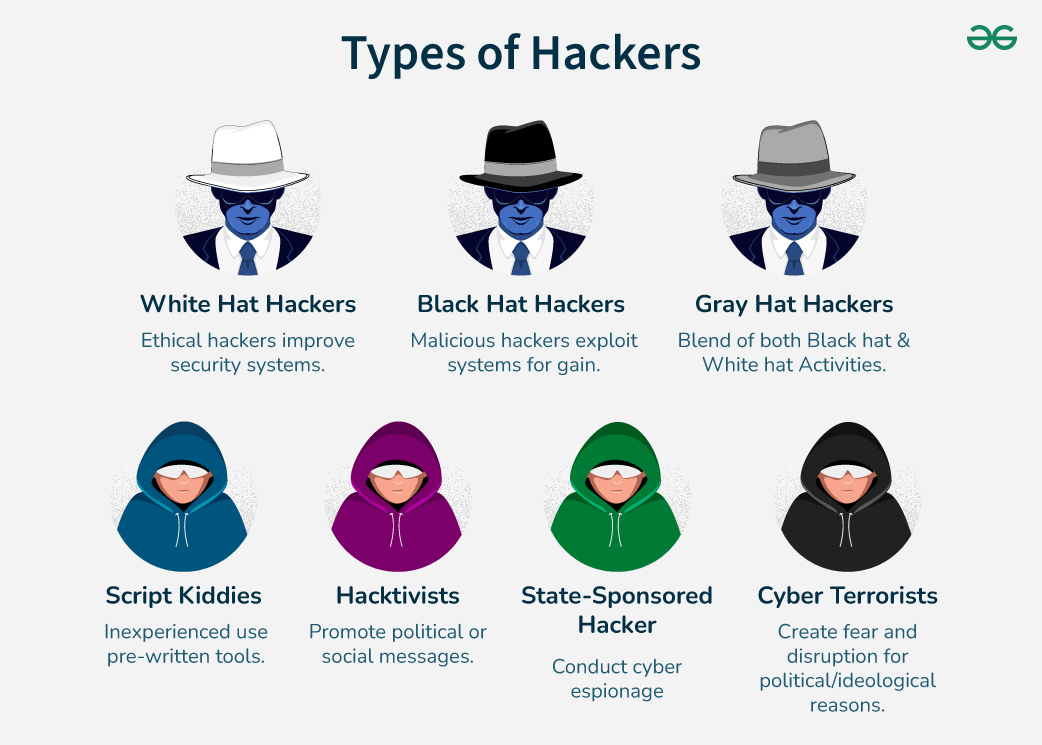
Other Types of Hackers
There are generally 7 types of Hackers, after the main 3 types, they are:
- Script Kiddies: They are the most dangerous people in terms of hackers. A Script kiddie is an unskilled person who uses scripts or downloads tools available for hacking provided by other hackers. They attempt to attack computer systems and networks and deface websites. Their main purpose is to impress their friends and society. Generally, Script Kiddies are juveniles who are unskilled about hacking.
- Green Hat Hackers: They are also amateurs in the world of hacking but they are bit different from script kiddies. They care about hacking and strive to become full-blown hackers. They are inspired by the hackers and ask them few questions about. While hackers are answering their question they will listen to its novelty.
- Blue Hat Hackers: They are much like the white hat hackers, they work for companies for security testing of their software right before the product launch. Blue hat hackers are outsourced by the company unlike white hat hackers which are employed by the (part of the) company.
- Red Hat Hackers: They are also known as the eagle-eyed hackers. Like white hat hackers, red hat hackers also aims to halt the black hat hackers. There is a major difference in the way they operate. They become ruthless while dealing with malware actions of the black hat hackers. Red hat hacker will keep on attacking the hacker aggressively that the hacker may know it as well have to replace the whole system.
- State/Nation Sponsored Hackers: State or Nation sponsored hackers are those who are appointed by the government to provide them cybersecurity and to gain confidential information from other countries to stay at the top or to avoid any kind of danger to the country. They are highly paid government workers.
- Hacktivist: These are also called the online versions of the activists. Hacktivist is a hacker or a group of anonymous hackers who gain unauthorized access to government’s computer files and networks for further social or political ends.
- Malicious Insider or Whistleblower: A malicious insider or a whistleblower could be an employee of a company or a government agency with a grudge or a strategic employee who becomes aware of any illegal activities happening within the organization and can blackmail the organization for his/her personal gain.
What are the types of Hacking?

There are different ways in which a system can be hacked –
1. Computer Hacking or System Hacking
This type of hacking includes illegally gaining access to individual systems or computers within a network. This is often seen when the target is singular, or the purpose is to steal information from a network of computers. It is the job of ethical hackers to try and get into the systems to identify the weak points.
2. Network Hacking or Wireless Network Hacking
Wireless Hacking is the process of stealing, capturing, or monitoring the wireless packets within a particular network. Once a hacker gets access to the wireless network, they can also access passwords, chat sessions, user history, etc. Ethical Hackers use similar methods to breach the wireless network and find new and different ways that Black Hat hackers can use.
3. Email Hacking
In the digital world of the corporate sector, emails contain extremely sensitive data & information that hackers may be interested in. Email hacking can include hacking into the network to get email passwords and gaining unauthorized access to the email of an individual or employees of a business. This can expose an individual’s personal life or reveal sensitive data from business emails. A phishing attack (widespread) can also lead to users compromising their personal information or data security.
4. Website Hacking or Web Application Hacking
Unethical hackers might show interest in hacking websites or web servers as it can negatively affect a business. This can lead to the website being down for extended periods (loss of business, exposure, and recognition), theft of software and database, and even permanent damage. However, ethical hackers attempt to do this with permission and then suggest how the cracks can be fixed.
5. Password hacking can be a part of computer or system hacking.
Hackers utilize the data stored on the computer and on the servers to access the passwords to any website, computer, email, accounts, etc., and then use that information for malicious purposes. Ethical hackers use similar methods to do so and identify any security measures that can be followed to prevent this.
Phases of Ethical Hacking

1. Reconnaissance
First in the ethical hacking methodology steps is reconnaissance, also known as the footprint or information gathering phase. The goal of this preparatory phase is to collect as much information as possible. Before launching an attack, the attacker collects all the necessary information about the target. The data is likely to contain passwords, essential details of employees, etc. An attacker can collect the information by using tools such as HTTPTrack to download an entire website to gather information about an individual or using search engines such as Maltego to research about an individual through various links, job profile, news, etc.
Reconnaissance is an essential phase of ethical hacking. It helps identify which attacks can be launched and how likely the organization’s systems fall vulnerable to those attacks.
Footprinting collects data from areas such as:
- TCP and UDP services
- Vulnerabilities
- Through specific IP addresses
- Host of a network
In ethical hacking, footprinting is of two types:
Active: This footprinting method involves gathering information from the target directly using Nmap tools to scan the target’s network.
Passive: The second footprinting method is collecting information without directly accessing the target in any way. Attackers or ethical hackers can collect the report through social media accounts, public websites, etc.
2. Scanning
The second step in the hacking methodology is scanning, where attackers try to find different ways to gain the target’s information. The attacker looks for information such as user accounts, credentials, IP addresses, etc. This step of ethical hacking involves finding easy and quick ways to access the network and skim for information. Tools such as dialers, port scanners, network mappers, sweepers, and vulnerability scanners are used in the scanning phase to scan data and records. In ethical hacking methodology, four different types of scanning practices are used, they are as follows:
Vulnerability Scanning: This scanning practice targets the vulnerabilities and weak points of a target and tries various ways to exploit those weaknesses. It is conducted using automated tools such as Netsparker, OpenVAS, Nmap, etc.
Port Scanning: This involves using port scanners, dialers, and other data-gathering tools or software to listen to open TCP and UDP ports, running services, live systems on the target host. Penetration testers or attackers use this scanning to find open doors to access an organization’s systems.
Network Scanning: This practice is used to detect active devices on a network and find ways to exploit a network. It could be an organizational network where all employee systems are connected to a single network. Ethical hackers use network scanning to strengthen a company’s network by identifying vulnerabilities and open doors.
3. Gaining Access
The next step in hacking is where an attacker uses all means to get unauthorized access to the target’s systems, applications, or networks. An attacker can use various tools and methods to gain access and enter a system. This hacking phase attempts to get into the system and exploit the system by downloading malicious software or application, stealing sensitive information, getting unauthorized access, asking for ransom, etc. Metasploit is one of the most common tools used to gain access, and social engineering is a widely used attack to exploit a target.
Ethical hackers and penetration testers can secure potential entry points, ensure all systems and applications are password-protected, and secure the network infrastructure using a firewall. They can send fake social engineering emails to the employees and identify which employee is likely to fall victim to cyberattacks.
4. Maintaining Access
Once the attacker manages to access the target’s system, they try their best to maintain that access. In this stage, the hacker continuously exploits the system, launches DDoS attacks, uses the hijacked system as a launching pad, or steals the entire database. A backdoor and Trojan are tools used to exploit a vulnerable system and steal credentials, essential records, and more. In this phase, the attacker aims to maintain their unauthorized access until they complete their malicious activities without the user finding out.
Ethical hackers or penetration testers can utilize this phase by scanning the entire organization’s infrastructure to get hold of malicious activities and find their root cause to avoid the systems from being exploited.
5. Clearing Track
The last phase of ethical hacking requires hackers to clear their track as no attacker wants to get caught. This step ensures that the attackers leave no clues or evidence behind that could be traced back. It is crucial as ethical hackers need to maintain their connection in the system without getting identified by incident response or the forensics team. It includes editing, corrupting, or deleting logs or registry values. The attacker also deletes or uninstalls folders, applications, and software or ensures that the changed files are traced back to their original value.
In ethical hacking, ethical hackers can use the following ways to erase their tracks:
- Using reverse HTTP Shells
- Deleting cache and history to erase the digital footprint
- Using ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol) Tunnels
These are the five steps of the CEH hacking methodology that ethical hackers or penetration testers can use to detect and identify vulnerabilities, find potential open doors for cyberattacks and mitigate security breaches to secure the organizations. To learn more about analyzing and improving security policies, network infrastructure, you can opt for an ethical hacking certification.
Conclusion:
Becoming a proficient ethical hacker requires a multifaceted approach that encompasses technical knowledge, practical skills, and a commitment to ethical conduct. By focusing on foundational concepts, programming skills, networking expertise, and staying informed about the latest developments in cybersecurity, you can build a strong foundation for a successful career in ethical hacking. Always approach ethical hacking with responsibility, ethical considerations, and a dedication to securing digital systems.


